Applications
Tags
Parameters
Related Products
- By
- Posted Thursday, August 15, 2024 - 09:30
By leveraging the strengths of both radar and INS, engineers and researchers can develop more capable and adaptable autonomous robots for a variety of applications, from industrial automation to autonomous vehicles.
Precise and reliable navigation is paramount for autonomous robots operating in complex environments. While Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) have been a cornerstone of outdoor navigation, their limitations in challenging conditions such as urban canyons, tunnels, or indoor spaces necessitate complementary technologies.
Radar and Inertial Navigation Systems (INS) offer a robust solution to these challenges. Radar, with its ability to penetrate adverse weather conditions and accurately measure range, velocity, and angle, provides valuable data for obstacle detection, environment mapping, and motion estimation. INS, on the other hand, offer continuous, high-rate measurements of acceleration and angular velocity, enabling accurate dead reckoning and short-term positioning.
By fusing radar and INS data, a more resilient and accurate navigation system can be achieved. Radar data can be used to correct INS drift, while INS data can provide initial estimates for radar-based tracking. This synergistic approach significantly improves navigation performance, especially in GPS-denied or degraded environments.

The MicroStrain 3DM-CV7-INS, with its ability to integrate various sensor inputs, including radar velocity measurements, offers a versatile platform for developing advanced navigation solutions. Our research demonstrates that integrating radar data with the CV7-INS can enhance navigation accuracy by up to 93% during GPS outages.
Key advantages of combining radar and INS for robot navigation include:
- Improved accuracy and reliability: Radar complements INS by providing independent measurements, reducing error accumulation and enhancing overall system robustness.
- Enhanced situational awareness: Radar's ability to detect objects in the environment provides crucial information for obstacle avoidance and path planning.
- Expanded operational capabilities: By mitigating the reliance on GPS, robots can operate more effectively in challenging environments.
- Cost-effectiveness: While radar systems have traditionally been expensive, recent advancements have made them more affordable, making them a viable option for a wider range of applications.
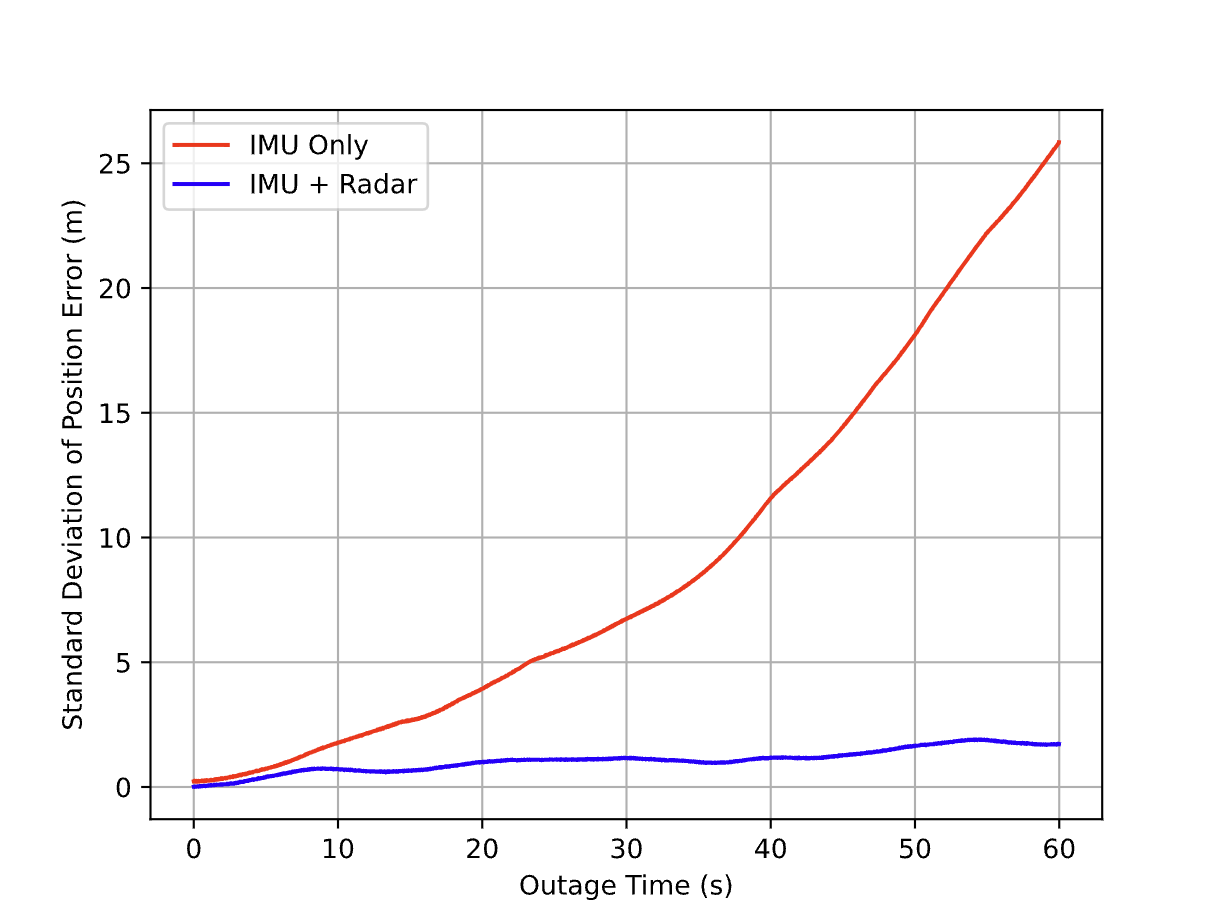
By leveraging the strengths of both radar and INS, engineers and researchers can develop more capable and adaptable autonomous robots for a variety of applications, from industrial automation to autonomous vehicles.
Download our white paper for a deeper dive into the technical details and performance evaluation of our radar and INS integration solution.
Related products: